The intersection of technology and medicine has always been a fertile ground for innovation, and 3D printing has emerged as a particularly promising field within healthcare. While the hype surrounding this technology can sometimes overshadow the practical realities, it’s essential to explore both the potential benefits and the inherent challenges that 3D printing presents in the medical arena.
The Ongoing Saga of 3D Printing in Healthcare

One of the most compelling applications of 3D printing in healthcare lies in the creation of patient-specific medical devices and implants. Traditional manufacturing methods often struggle to produce items that perfectly match the unique anatomy of each individual. 3D printing, however, allows for the creation of custom-designed prosthetics, implants, and surgical guides, leading to improved fit, functionality, and patient outcomes. This personalized approach has the potential to revolutionize various surgical procedures, from joint replacements to craniofacial reconstruction.
Beyond implants, 3D printing is making inroads in the production of anatomical models for surgical planning. Surgeons can now use these models to rehearse complex procedures before entering the operating room, allowing them to anticipate potential challenges and optimize their approach. This can reduce surgery time, minimize risks, and ultimately improve patient safety. Moreover, these models can be used for educational purposes, providing medical students and residents with a hands-on learning experience that enhances their understanding of complex anatomical structures.
The pharmaceutical industry is also exploring the potential of 3D printing to create customized drug formulations. Imagine a future where medications are tailored to an individual’s specific needs and genetic makeup, ensuring optimal efficacy and minimizing side effects. While this vision is still in its early stages, researchers are actively working on developing 3D-printed pills that can deliver precise dosages of multiple drugs in a single tablet. This could significantly improve patient adherence to medication regimens, particularly for those with complex medical conditions requiring multiple prescriptions.
3D printing in healthcare. The potential and the pitfalls.
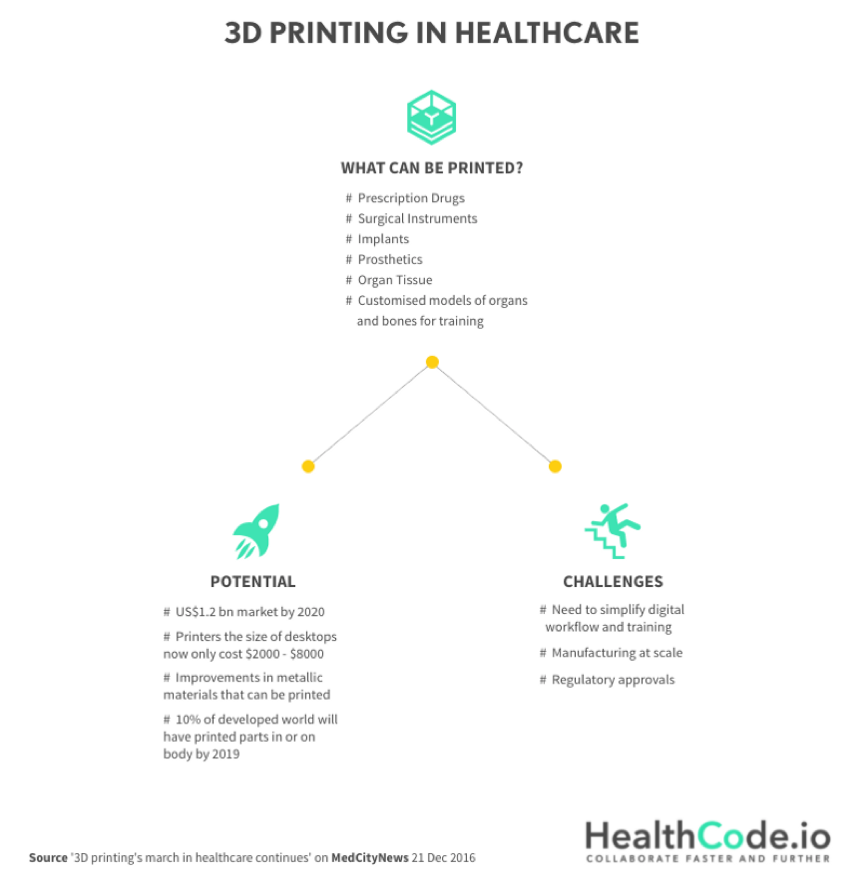
Despite the immense potential, several challenges need to be addressed before 3D printing can be fully integrated into mainstream healthcare. One major hurdle is the regulatory landscape. As a relatively new technology, 3D printing lacks clear and comprehensive regulatory guidelines, particularly concerning the manufacturing and quality control of medical devices. Establishing robust regulatory frameworks is crucial to ensure the safety and efficacy of 3D-printed medical products. Without clear guidelines, manufacturers may be hesitant to invest in the technology, hindering its widespread adoption.
Another significant challenge is the cost of 3D printing. While the technology has become more affordable in recent years, the cost of materials, equipment, and specialized expertise can still be prohibitive for many healthcare providers, especially in resource-constrained settings. Further advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes are needed to reduce the cost of 3D printing and make it more accessible to a wider range of healthcare facilities.
Finally, the need for skilled personnel is paramount. Operating and maintaining 3D printing equipment requires specialized training and expertise. Healthcare professionals need to be educated about the capabilities and limitations of 3D printing, and engineers and technicians need to be trained in the design, fabrication, and post-processing of 3D-printed medical devices. Investing in training and education programs is essential to build a skilled workforce capable of driving the adoption of 3D printing in healthcare.
In conclusion, 3D printing holds tremendous promise for transforming healthcare, offering the potential to personalize medicine, improve surgical outcomes, and revolutionize drug delivery. However, overcoming the regulatory, cost, and training challenges is crucial to unlocking its full potential and ensuring that this innovative technology benefits patients worldwide.
If you are searching about Is 3D Printing in Healthcare the Start of a Medical Revolution you’ve visit to the right place. We have 10 Pics about Is 3D Printing in Healthcare the Start of a Medical Revolution like Stream episode 7 Major Challenges of 3D Printing In Healthcare by, 3D Printing – Analysis of Innovative Technology in the Health Sector and also Stream episode 7 Major Challenges of 3D Printing In Healthcare by. Here you go:
Is 3D Printing In Healthcare The Start Of A Medical Revolution

healthtechmagazine.net
printing 3d medical healthtech manufacturing igem prosthetics newsletter healthcare healthtechmagazine munich lmu tum
The Role Of 3D Printing In Health – Digital Brunei

digitalbrunei.bn
3D Printing – Analysis Of Innovative Technology In The Health Sector

technew.com.au
3 Ways 3D Printing Is Revolutionizing Health Care | AHA

www.aha.org
3D Printing In Healthcare. The Potential And The Pitfalls. | By

medium.com
(PDF) 3D Printing Applied To Health

www.researchgate.net
The Ongoing Saga Of 3D Printing In Healthcare | HealthTrip

www.healthtrip.com
Stream Episode 7 Major Challenges Of 3D Printing In Healthcare By

soundcloud.com
3D Printing & Their Impact | Health 2.0 Conference

www.health2conf.com
McMaster HealthTech – Innovation At The Intersection Of Technology And
machealthtech.ca
Is 3d printing in healthcare the start of a medical revolution. 3d printing & their impact. 3d printing





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/008_how-to-factory-reset-a-lenovo-laptop-5115817-a67348722ce94f9783881ea29e596310.jpg)